Balloon valvuloplasty, also known as BAV, BPV, or BMV, is a critical procedure used to improve heart function in patients with narrowed heart valves. This minimally invasive technique utilizes a balloon catheter to open narrowed valves, allowing for better blood flow and reducing symptoms caused by valvular disease. Dr. Prem Ratan Degawat, a renowned interventional cardiologist, is dedicated to helping patients regain their quality of life through procedures like balloon valvuloplasty. His expertise ensures this procedure is performed with precision and care, aiming for optimal cardiac function and a return to a healthier lifestyle.
Balloon Valvuloplasty:
Balloon valvuloplasty is a minimally invasive procedure performed by interventional cardiologists. It is primarily indicated for patients suffering from valve stenosis, where the valve leaflets become thickened or fused, reducing the valve’s ability to open and close properly. This condition can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue.
Types of Balloon Valvuloplasty:
There are major 3 types of balloon valvuloplasty procedures, each tailored to specific heart valves and conditions:
- Mitral Valve Balloon Valvuloplasty (BMV)
BMV is used to treat mitral valve stenosis, a condition where the mitral valve, located between the left atrium and left ventricle, becomes narrowed. During the procedure, a balloon catheter is guided to the mitral valve through a vein in the groin or arm. The balloon is then inflated, stretching the valve opening and improving blood flow.
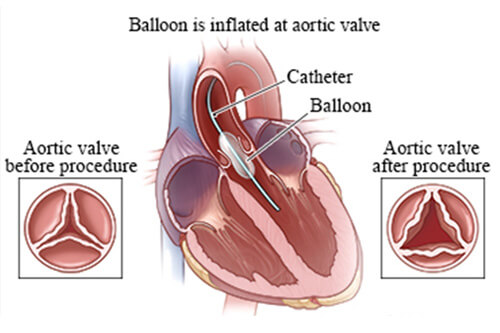
- Aortic Valve Balloon Valvuloplasty (BAV)
BAV is performed to treat aortic valve stenosis, which affects the valve between the left ventricle and the aorta. This procedure follows a similar approach as BMV, where the balloon catheter is inserted into the narrowed valve and inflated to widen the valve opening, thus enhancing cardiac output.
- Pulmonary Valve Balloon Valvuloplasty (BPV)
BPV targets stenosis of the pulmonary valve, which regulates blood flow from the heart’s right ventricle to the lungs. By using a balloon catheter to dilate the narrowed pulmonary valve, BPV improves blood flow dynamics and reduces symptoms associated with pulmonary valve stenosis.
Benefits of Balloon Valvuloplasty:
- Minimally Invasive Nature
One of the primary advantages of balloon valvuloplasty is its minimally invasive nature compared to traditional open-heart surgery. This results in shorter recovery times, reduced hospital stays, and lower risks of complications such as infection and bleeding.
- Symptom Relief
Balloon valvuloplasty effectively relieves symptoms associated with valve stenosis, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue. By improving blood flow through the affected valve, patients experience enhanced exercise tolerance and overall quality of life.
- Preservation of Valve Structure
Unlike valve replacement surgeries, which involve replacing the diseased valve with a prosthetic valve, balloon valvuloplasty preserves the patient’s natural valve structure. This can be particularly beneficial for younger patients or those with complex medical histories where valve replacement may pose higher risks.
Risks and Complications:
While balloon valvuloplasty is generally considered safe, there are inherent risks and potential complications associated with the procedure:
- Valve Regurgitation: In some cases, balloon inflation may cause valve leaflet damage, leading to valve leakage or regurgitation.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms may occur during or after the procedure, requiring monitoring and potential treatment.
- Vascular Injury: There is a small risk of damage to blood vessels at the catheter insertion site, which can result in bleeding or hematoma formation.
- Stroke: Rarely, emboli dislodged during the procedure may travel to the brain, causing a stroke.
Candidate Selection and Pre-procedural Assessment:
- Patient Evaluation
Before recommending balloon valvuloplasty, thorough patient evaluation is essential. This includes reviewing medical history, performing physical examinations, and conducting diagnostic tests such as echocardiography and cardiac catheterization to assess the severity of valve stenosis and overall cardiac function.
- Procedural Planning
Once a patient is identified as a suitable candidate for balloon valvuloplasty, procedural planning begins. This involves selecting the appropriate type of valvuloplasty based on the affected valve and the severity of stenosis. Detailed imaging studies aid in determining the optimal approach for catheter placement and balloon inflation.
Procedure Steps:
- Anesthesia and Access
The procedure typically begins with the administration of local anesthesia and sedation to ensure patient comfort. A small incision is made in the groin or arm to access the blood vessel through which the balloon catheter will be inserted.
- Catheter Insertion and Guidance
Under fluoroscopic guidance, the balloon catheter is carefully advanced through the blood vessel and positioned at the site of the narrowed valve. Fluoroscopy provides real-time imaging of the catheter’s movement, ensuring precision during the procedure.
- Balloon Inflation
Once the catheter is in the correct position, the balloon at its tip is inflated. The inflation process compresses the valve leaflets against the valve annulus, stretching the narrowed opening and improving blood flow through the valve.
- Deflation and Catheter Removal
After achieving the desired valve dilation, the balloon is deflated and withdrawn from the body. The small incision made for catheter insertion is then closed with sutures or adhesive strips, marking the conclusion of the procedure.
Meet the Expert: Dr. Prem Ratan Degawat, Interventional Cardiologist in Jaipur, Rajasthan
Dr. Prem Ratan Degawat is a leading interventional cardiologist in Jaipur, Rajasthan. He is a beacon of expertise in the field, particularly known for his work as a best balloon valvuloplasty cardiologist and a balloon valvuloplasty aortic doctor in Jaipur, Rajasthan. Dr. Degawat’s passion lies in advancing cardiac care, and he dedicates his career to helping patients overcome heart challenges with cutting-edge procedures like balloon valvuloplasty. Additionally, as a TAVI Expert in Rajasthan, Dr. Degawat is committed to providing the highest level of care to his patients.
Conclusion
Balloon valvuloplasty (BAV, BPV, BMV) is a valuable intervention for patients suffering from valvular stenosis, offering significant benefits in symptom relief and cardiac function improvement. This minimally invasive procedure, performed by skilled interventional cardiologists, continues to play a pivotal role in modern cardiology, providing patients with a path to better heart health and enhanced quality of life.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Prem Ratan Degawat, renowned as the Best Cardiologist in Jaipur and Heart Valve Expert in Rajasthan.
✆ Book your appointment and take the first step towards better heart health
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Balloon Valvuloplasty:
- What conditions does balloon valvuloplasty treat?
Balloon valvuloplasty is primarily used to treat valve stenosis, where heart valves become narrowed due to thickening or fusion of valve leaflets. It is commonly performed for mitral valve stenosis (BMV), aortic valve stenosis (BAV), and pulmonary valve stenosis (BPV).
- How is balloon valvuloplasty performed?
The procedure involves inserting a balloon-tipped catheter into a blood vessel, typically in the groin or arm, and guiding it to the affected heart valve under fluoroscopic guidance. Once positioned, the balloon is inflated to stretch the narrowed valve, improving blood flow.
- How long does balloon valvuloplasty take to perform?
Balloon valvuloplasty typically takes about 1 to 2 hours to complete, depending on the complexity of the case and the patient’s specific condition.
- How long does a balloon aortic valvuloplasty last?
The longevity of balloon valvuloplasty results can vary depending on the severity of the initial valve narrowing and individual patient factors. In some cases, the effects may last for several years, while others may experience valve re-narrowing within 6 months. Regular follow-up with your doctor is crucial to monitor the valve function.
- How successful is balloon valvuloplasty?
Balloon valvuloplasty can be a successful procedure for some patients, especially those with milder valve narrowing or those at high risk for surgery. Success rates can vary depending on the specific valve being treated and the patient’s condition. Generally, the procedure improves symptoms like shortness of breath and chest pain, and allows for better blood flow through the heart.
- What are the benefits of balloon valvuloplasty compared to valve replacement?
Balloon valvuloplasty is less invasive than valve replacement surgery, resulting in shorter recovery times and reduced risks of complications such as infection and bleeding. It also preserves the patient’s natural valve structure, which can be advantageous in certain cases.
- Who is a suitable candidate for balloon valvuloplasty?
Candidates for balloon valvuloplasty undergo thorough evaluation, including medical history review, physical examinations, and imaging tests (e.g., echocardiography). Ideal candidates typically have symptomatic valve stenosis without significant valve damage or other contraindications.
- Are there alternatives to balloon valvuloplasty?
For patients with severe valve disease or complex conditions, alternatives such as transcatheter valve replacement (TAVR) or surgical valve replacement may be considered. These options are tailored based on individual patient factors and the specific type of valve disease.
- How soon can patients resume normal activities after balloon valvuloplasty?
Recovery times vary, but many patients can resume normal activities within a few days to a week after the procedure. Dr. Degawat provides personalized post-procedure instructions to optimize recovery.
- What should I expect during the recovery period?
During recovery, patients may experience improvements in symptoms such as reduced chest pain and improved breathing. It’s essential to follow Dr. Degawat’s recommendations for medication, lifestyle adjustments, and follow-up appointments to support long-term heart health.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge only and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider to discuss your individual circumstances and treatment options.