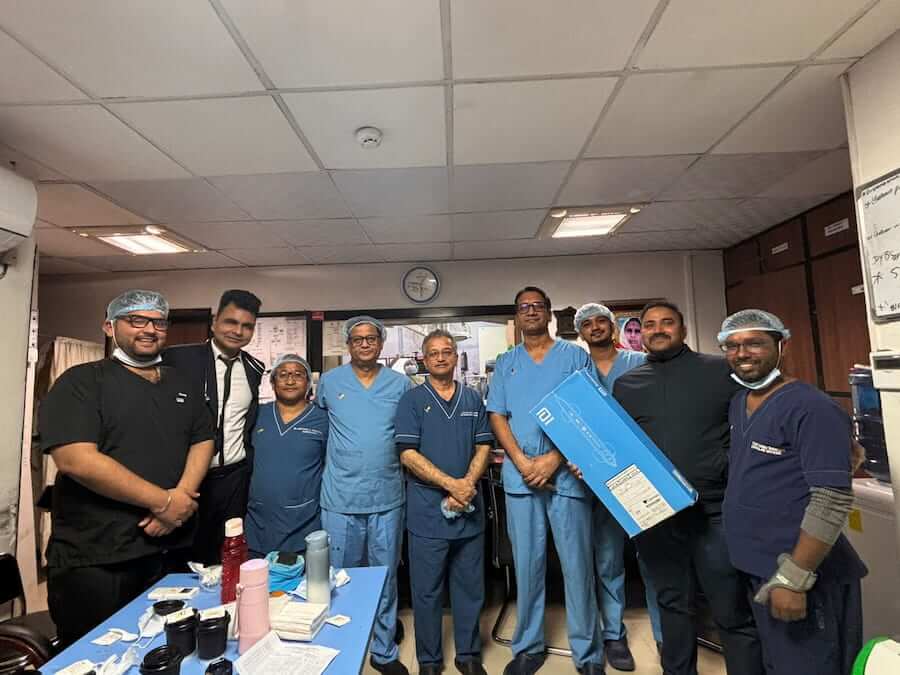
A significant milestone in interventional cardiology was achieved with the successful completion of Nepal’s first Orbital Atherectomy procedure in Kathmandu.
The case was proctored by Dr. Prem Ratan Degawat, reinforcing the growing adoption of advanced coronary calcium management techniques in complex cardiac care.
This achievement represents not only technical excellence but also the strengthening of expertise in managing challenging coronary artery disease.
Understanding the Challenge: Calcified Coronary Arteries
Coronary artery disease becomes particularly complex when arteries are heavily calcified. Calcium deposits make the artery rigid and narrow, which can:
- Reduce blood flow to the heart
- Make stent delivery difficult
- Increase procedural complexity
- Affect long-term treatment outcomes
In such cases, conventional angioplasty may not be sufficient. Specialized plaque-modifying technologies are required.
What is Orbital Atherectomy?
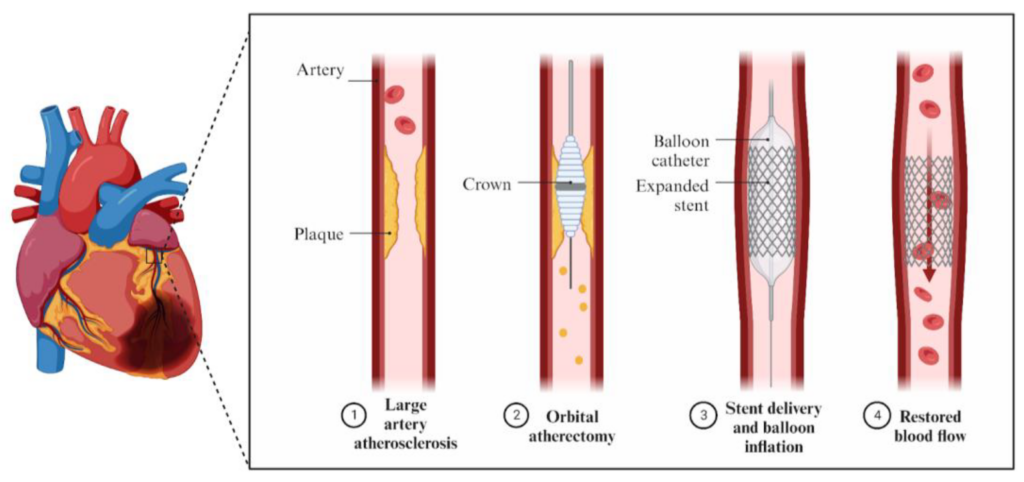
Orbital Atherectomy is an advanced technique used to modify hardened calcium within coronary arteries before stent placement.
Unlike traditional balloon angioplasty, this technology:
- Sands down and modifies calcified plaque
- Improves vessel compliance
- Enhances stent expansion
- Reduces procedural complications
By preparing the artery properly, it significantly improves the chances of optimal long-term results.
The Historic Procedure in Kathmandu
The successful completion of Nepal’s first Orbital Atherectomy marks an important step in complex coronary intervention capability within the country.
Serving as Proctor, Dr. Prem Ratan Degawat provided procedural guidance, clinical expertise, and strategic decision-making support throughout the case. The outcome reflects:
- Strong team coordination
- Advanced cath lab infrastructure
- Skilled interventional execution
- Commitment to high-quality cardiac care
Such milestones elevate the standard of complex heart procedures and open pathways for managing more challenging cases locally.
Why This Milestone Matters
The introduction of advanced calcium modification techniques means:
- Patients with severe calcification can be treated more effectively
- Fewer referrals outside the region for complex cases
- Improved procedural confidence for interventional teams
- Expansion of high-end cardiac capabilities
It signals progress in structural and interventional cardiology and strengthens the ecosystem of advanced cardiac care.
Commitment to Advancing Cardiac Care
Milestones like Nepal’s first Orbital Atherectomy demonstrate how collaboration, expertise, and innovation come together to improve patient outcomes.
Under the leadership and mentorship of experts like Dr. Prem Ratan Degawat, advanced interventional techniques continue to reach new frontiers enabling better management of complex coronary disease and improving lives, one heartbeat at a time.
FAQs:
1. What is coronary artery calcification?
It is the buildup of hardened calcium deposits inside the heart’s arteries, making them stiff and narrowed.
2. Why is calcification a problem during angioplasty?
Calcified arteries resist balloon expansion and may prevent proper stent placement, increasing procedural risk.
3. How does Orbital Atherectomy help?
It modifies and smoothens the calcium, allowing better stent expansion and improved blood flow restoration.
4. Is Orbital Atherectomy safe?
When performed by experienced interventional cardiologists, it is a safe and effective technique for selected patients.
5. Who may need this procedure?
Patients with severe, heavily calcified coronary artery disease identified during angiography may benefit from it.